The hardware platform is based on the original two-motor XRP chassis, upgraded with ultrasonic distance sensors, infrared line sensors, and optional servo-mounted components. Custom motor drivers and reinforced frames improve precision and stability, allowing the robot to navigate more complex courses and carry small payloads for testing. Programmable LED indicators provide visual feedback for sensor readings and control states, helping learners understand how the robot interprets its environment.
Programming is implemented using Python and MicroPython frameworks, enabling experiments with PID motor control, autonomous navigation, and sensor fusion. Students can program the robot to follow lines, avoid obstacles, and execute predefined patterns while monitoring real-time sensor data. Wireless modules allow for remote control and telemetry logging, making it possible to test and optimize behaviors in dynamic environments.
This project demonstrates the process of customizing an educational robotics platform for deeper learning and experimentation. By combining modular hardware, programmable controls, and interactive feedback, it provides a rich, hands-on experience that teaches robotics, embedded systems, and iterative design principles in a single, adaptable platform.
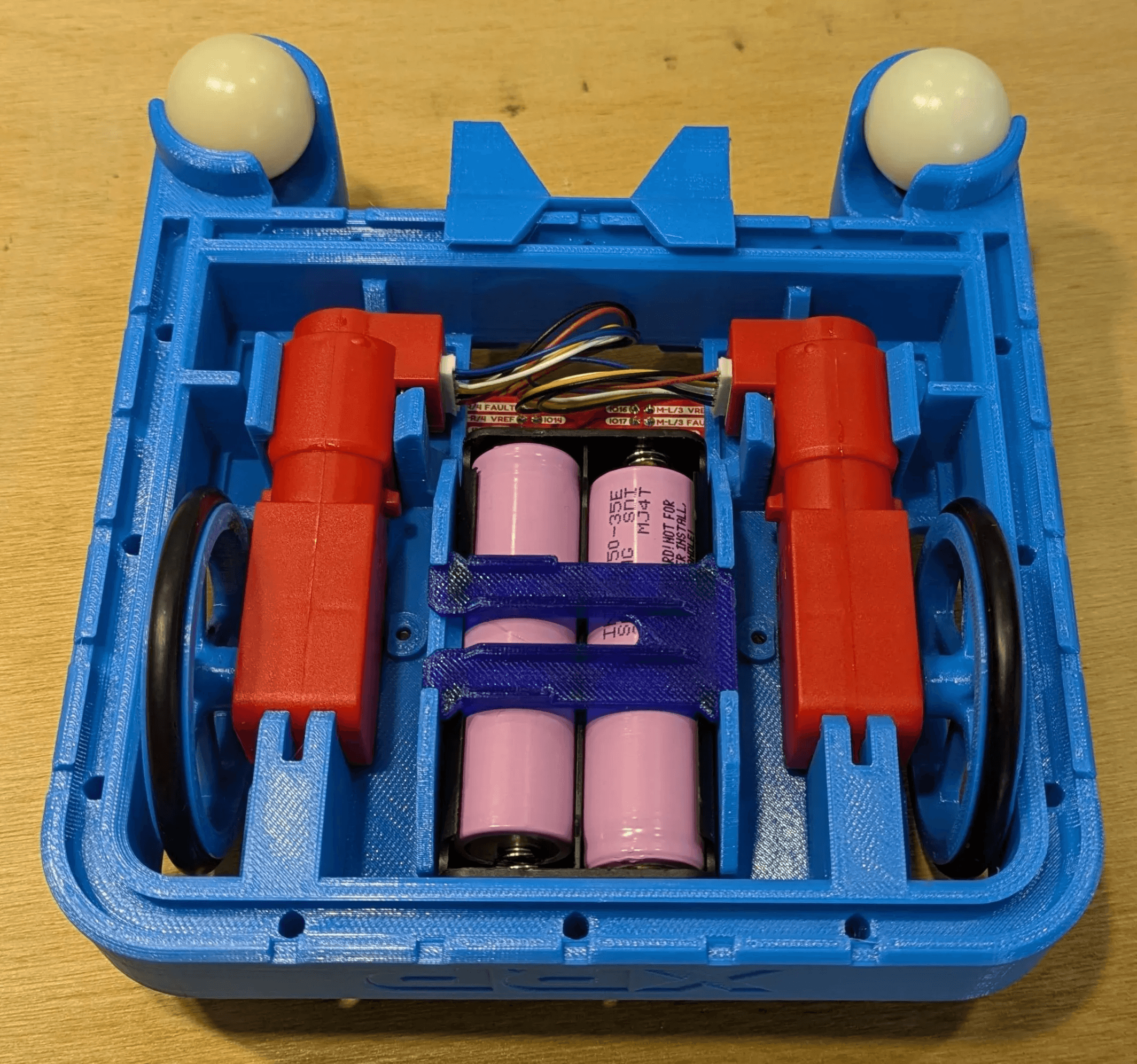
The hardware platform is based on the original two-motor XRP chassis, upgraded with ultrasonic distance sensors, infrared line sensors, and optional servo-mounted components. Custom motor drivers and reinforced frames improve precision and stability, allowing the robot to navigate more complex courses and carry small payloads for testing. Programmable LED indicators provide visual feedback for sensor readings and control states, helping learners understand how the robot interprets its environment.
Programming is implemented using Python and MicroPython frameworks, enabling experiments with PID motor control, autonomous navigation, and sensor fusion. Students can program the robot to follow lines, avoid obstacles, and execute predefined patterns while monitoring real-time sensor data. Wireless modules allow for remote control and telemetry logging, making it possible to test and optimize behaviors in dynamic environments.
This project demonstrates the process of customizing an educational robotics platform for deeper learning and experimentation. By combining modular hardware, programmable controls, and interactive feedback, it provides a rich, hands-on experience that teaches robotics, embedded systems, and iterative design principles in a single, adaptable platform.

The hardware platform is based on the original two-motor XRP chassis, upgraded with ultrasonic distance sensors, infrared line sensors, and optional servo-mounted components. Custom motor drivers and reinforced frames improve precision and stability, allowing the robot to navigate more complex courses and carry small payloads for testing. Programmable LED indicators provide visual feedback for sensor readings and control states, helping learners understand how the robot interprets its environment.
Programming is implemented using Python and MicroPython frameworks, enabling experiments with PID motor control, autonomous navigation, and sensor fusion. Students can program the robot to follow lines, avoid obstacles, and execute predefined patterns while monitoring real-time sensor data. Wireless modules allow for remote control and telemetry logging, making it possible to test and optimize behaviors in dynamic environments.
This project demonstrates the process of customizing an educational robotics platform for deeper learning and experimentation. By combining modular hardware, programmable controls, and interactive feedback, it provides a rich, hands-on experience that teaches robotics, embedded systems, and iterative design principles in a single, adaptable platform.









